Do LED Lights Get Hot? (2024 Updated)
LED lighting has revolutionized illumination across residential, commercial and industrial applications. But one enduring myth is that LEDs don’t produce heat. The reality is more nuanced - keep reading to understand how and why LEDs generate heat, the key factors affecting thermal performance, and most importantly, best practices to manage LED heat for optimal efficiency, lifespan and safety.
How Do LED Lights Produce Heat?
To generate light, LEDs pass current through a semiconductor material in a process called electroluminescence. Some input electrical energy inevitably gets converted to heat instead of light. There are two primary sources of heat in an LED:
- The LED Chip: At the microscopic scale, passing current through the LED chip junction generates heat. Higher drive currents mean more light output, but also increased junction heating.
- The LED Driver: The driver electronics regulate power to the LED. Converting and delivering energy to the LED chips produces heat in driver components. Higher wattage drivers run hotter.
In addition, some heat gets absorbed by external surfaces like the bulb housing and fixture body.
So in summary, LEDs convert electricity to both light and heat due to basic physics. This sets them apart from traditional incandescent bulbs that emit mostly infrared radiation. The key is managing LED heat generation through proper thermal design.
Factors Affecting LED Heat Levels
These four interdependent factors determine how hot an LED operates:
LED Wattage Rating
Higher wattage equals more electricity input to LED chips. More power = more light emission = more heat generation. For example, a 9W LED bulb runs cooler than a 15W version with more chips at higher drive currents.
Overdriving an LED past its rated wattage also causes excessive heat and accelerated failures.
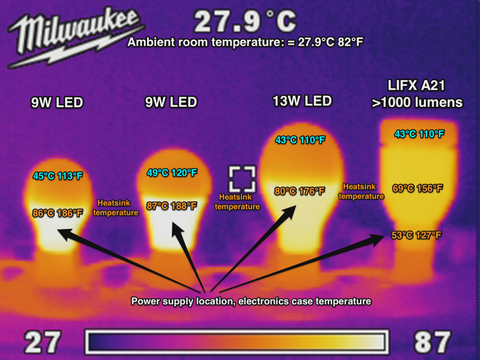
Ambient Temperature
Warmer ambient conditions reduce the LED’s ability to cool itself through convection. An LEDbulb in a 95°F attic shed less heat than one in a 68°F room.
Airflow and Ventilation
Moving airflow carries heat away from the LED through convection. Well-ventilated fixtures like open lamps allow airflow cooling. Tight enclosed housings trap and concentrate heat around the LED.
LED Encapsulant Material
The LED encapsulant transfers heat from the junction to the outer packaging. Quality silicone encapsulants optimize heat conduction. Plastics act more as insulators resulting in LED overheating.
With smart thermal design and component selection, LED heat can be appropriately managed as outlined below.
Is Heat From LED Lights Dangerous?
While LEDs run cooler than other bulb types, excessive heat poses risks:
- Fire hazard: Faulty LED drivers and inadequate heat sinking can lead to catastrophic failures. Always choose safety-certified products.
- Reduced lifespan: Heat accelerates lumen depreciation and shortens LED lifetime. Overdriving accelerates this effect.
- Burn hazard: Enclosed fixtures with poorly designed LED retrofits could overheat and pose a contact hazard.
However, with intelligent thermal management, these risks can be minimized for safe LED operation.
Managing LED Heat Levels
Here are tips to optimize LED heat dissipation and prevent overheating:
-
Select the right LED wattage for ambient conditions and allow overhead for future upgrades.
-
Validate luminaire housing design with thermal modeling before production.
-
Ensure adequate ventilation and airflow around the LED and housing.
-
Use a heat sink directly connected to the LED module if heat dissipation is inadequate.
-
Choose high conductivity silicone encapsulants to transfer heat effectively.
-
Mount LED modules on thermally conductive PCBs to spread heat laterally.
-
Use cooling fans or active liquid cooling for high-power LED arrays.
-
Monitor temperatures with sensors and shut down LEDs before excess heating.
With good thermal management and design validation, LEDs can deliver decades of low-maintenance operation.
LED Thermal Management Techniques
Let’s explore some key techniques to manage LED heating in more depth:
1. Heat Sinks
Heat sinks are devices designed to absorb and dissipate heat. They are commonly used with high-power LEDs and arrays. Key concepts include:
- Thermal resistance - measures how well heat transfers between two surfaces. Lower resistance equals better dissipation.
- Convection - moving air carries heat away from fins and surfaces. Fans improve forced convection.
- Radiation - heat radiates from hot surfaces to cooler surroundings according to material emissivity.
- Conduction - heat spreads through direct contact. Copper and aluminum are excellent conductors.
Large surface area fins maximize convection and radiation cooling. Heat pipes further enhance conductivity.
Well-designed LED heat sinks keep junction temperatures in check for optimal performance.
2. Metal Core PCBs
Metal core PCBs (MCPCB) conduct heat better than standard FR4 PCBs. Aluminum or copper substrate PCBs with dielectric insulation spread LED heat laterally. This lowers junction temperatures for array-based designs.
![LED star MCPCB][]
Aluminum MCPCB LED array with star layout. Credit: LED Professional
3. Encapsulation Material
LED encapsulants protect chips and conduct heat away from the junctions. Silicone encapsulants perform better than plastics. However, under high temperatures and UV light, silicone can yellow and become less transparent.
Epoxy and glass encapsulants withstand higher temperatures with better light transmission. This improves lifespan in high ambient environments like automotive lighting.
4. Thermal Interface Material
Thermal interface materials (TIM) placed between surfaces enhance heat transfer. They fill air gaps that impede conduction.
Common TIMs include thermally conductive pads, greases, gels and adhesives. They lower thermal resistance by directly bonding heat-generating and heat-sinking components.
5. Active Cooling
Fans and liquid cooling systems actively remove heat using convection. Heat pipes and vapor chambers transport heat to external surfaces. These active cooling methods sustain high luminous flux outputs from LED arrays used in automotive, aerospace and specialty lighting applications.
With good engineering, LED heat can be dissipated to enable many years of reliable illumination.
Thermal Design Process
Here is a typical LED thermal design process:
- Estimate initial heat load based on LED wattage, ambient temperature and duty cycle.
- Create thermal model with housing, heat sink, airflow and interfaces. Simulate temperatures.
- Evaluate results against target LED junction temperature and lifespan goals.
- Iterate on design by adjusting heat sink sizing, ventilation, interface materials, active cooling and other parameters.
- Build and test prototype to validate model accuracy. Refine design if needed.
- Perform accelerated life testing to confirm expected LED lifespan.
- Monitor temperatures in real-world installations to catch any issues.
With simulations correlated to measured data, LED fixtures can be optimally engineered for their deployment environments.
LED Lighting Lifespan and Temperature
Thermal management directly impacts LED product lifetimes. Consider these effects:
- LED lumen depreciation and color shift increase at higher junction temperatures.
- Operating LEDs at 50% of maximum temperature can increase lifespan by 10 to 20 times.
- Excessive cycling between high and low temperatures accelerates failures due to material expansion stresses.
- LED drivers also wear out faster when running hot.
Keep junction temperatures low to maximize LED lifespan and return on investment.
Conclusion
While LEDs run cooler than other lighting technologies, heat generation plays a critical role in product reliability and safety. With intelligent engineering of heat sinking, PCB and encapsulant materials, junction temperatures can be kept in check to achieve exceptional LED lifespan. Thermal design tools allow accurate modeling of LED systems to fine-tune heat dissipation performance. Advanced cooling methods enable high-power and high-density LED operation. By considering thermal effects early in the design process, LED lighting can deliver outstanding illumination.
If you're interested in LED bulk orders from China, contact Halcon Lighting now!







